 According to the Center for Disease Control (CDC) nearly half of American adults (47.2 percent) aged 30 and older have periodontal disease, otherwise known as gum disease. For adults 65 and over, this number rises to 70.1 percent. Gum disease is a chronic inflammatory disease affecting the gum tissue and the underlying bone. Since this condition can lead to tooth loss if left untreated, it is very important to take good care of your teeth and gums, brushing, flossing and rinsing at least twice a day. The American Academy of Periodontology recommends an annual visit for a periodontal evaluation. It is also critical to recognize symptoms of gum disease, so that if you suspect a serious problem, you can see your dentist right away.
According to the Center for Disease Control (CDC) nearly half of American adults (47.2 percent) aged 30 and older have periodontal disease, otherwise known as gum disease. For adults 65 and over, this number rises to 70.1 percent. Gum disease is a chronic inflammatory disease affecting the gum tissue and the underlying bone. Since this condition can lead to tooth loss if left untreated, it is very important to take good care of your teeth and gums, brushing, flossing and rinsing at least twice a day. The American Academy of Periodontology recommends an annual visit for a periodontal evaluation. It is also critical to recognize symptoms of gum disease, so that if you suspect a serious problem, you can see your dentist right away.
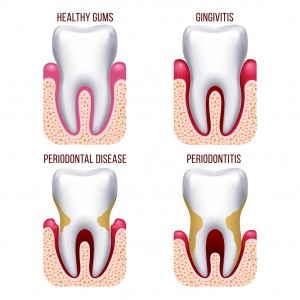
Types of Gum Disease
The mildest form of gum disease is gingivitis. It causes redness, inflammation of the gums and irritation, and it can be prevented with good dental health habits. This includes brushing your teeth and gums twice a day and seeing your dentist regularly for exams and thorough cleanings. If untreated gingivitis can lead to periodontitis, which is a more advanced gum infection. In addition to a decaying of the bones that support your teeth and possible tooth loss, periodontitis may also increase the risk of a heart attack, stroke or some other serious health issue.
Risk Factors of Developing Gum Disease
Poor oral hygiene is a main cause of gum disease, but there are other risk factors, including tobacco chewing or smoking, crooked teeth that are difficult to keep clean, pregnancy, diabetes, certain kinds of medications and genetics.
Early Symptoms of Gum Disease
Here are 7 symptoms of the beginning of gum disease, as stated by the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research and Medicine.Net, to be on the lookout for.
1. Bad breath or a bad taste in your mouth that doesn’t go away
2. Red, swollen or tender gums that bleed easily, even during simple brushing or flossing
3. Painful teeth and gums while chewing
4. Receding gums or teeth appear longer than normal
5. Sensitive teeth, especially with hot or cold foods
6. Loose or separating permanent teeth
7. Any change in your bite (how your teeth fit together)
Treatment Options for Gum Disease
If you have any of these symptoms, it is very important that you schedule a visit to your dentist right away. They will be able to do a comprehensive evaluation, point out problem areas and give you the best advice on how to treat it. Depending upon your situation and how severe the infection is, they might suggest a deep cleaning, medications, or as a last resort, surgical treatments. Deep cleaning is done by scaling and root planing, and this is done by a dentist, dental hygienist or periodontist. Medications may include a prescription antimicrobial mouthwash, antiseptic gelatin chip or antibiotic gel, among other possibilities. The purpose of these is to control bacteria and reduce the size of the periodontal pockets that have formed. There are also surgical options, should all else fail.
However, all this can be avoided by practicing healthy dental hygiene right now!






Leave a Reply